|
 Voie Domitienne - Grabels, France
N 43° 38.659 E 003° 49.383
31T E 566380 N 4832698
La voie Domitienne à Grabels
Waymark Code: WMXTBR
Location: Occitanie, France
Date Posted: 02/24/2018
Views: 11
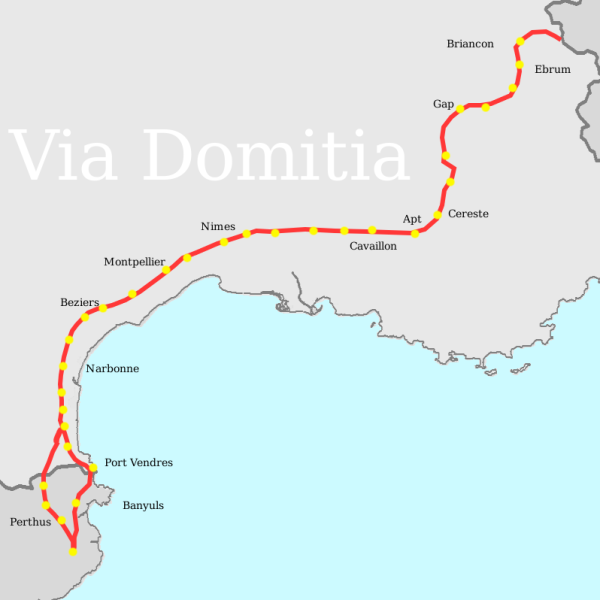
Source : https://fr.wikipedia.org/wiki/Voie_Domitienne
Bonus: La zone en photo à 360°
Most Relevant Historical Period: Roman Republic 509 B.C. - 27 B.C.

Admission Fee: 0

Condition: Some remaining traces (ruins) or pieces

Opening days/times: Not listed

Web Site: Not listed

|
Visit Instructions:
A complete sentence or two or an uploaded photo taken by the waymarker will be required in the log to confirm that the logger is participating in the hobby in good faith. Logs of only a few words like "Visited it" without an original photo are subject to deletion.
|